Answer of September 2010
Clinical History:
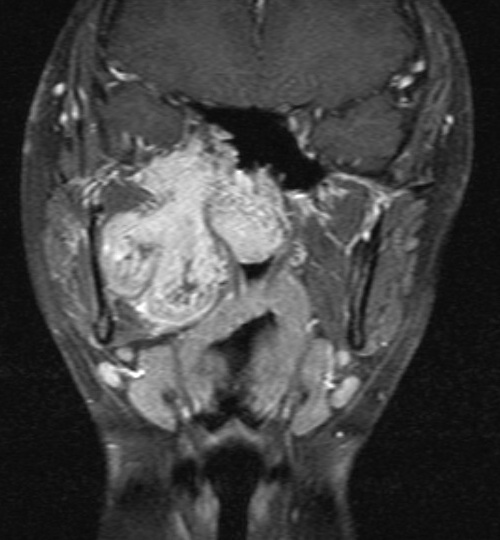
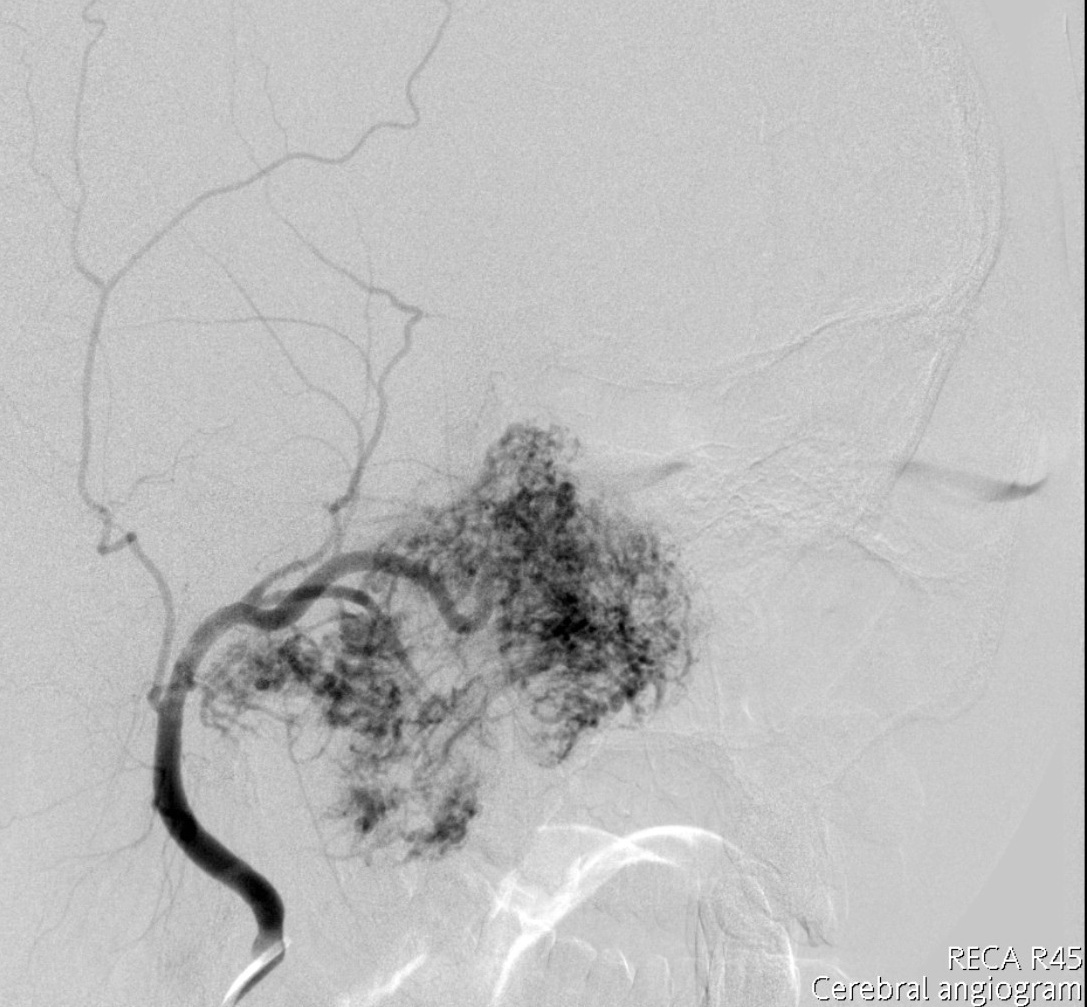
A 16 years-old boy was presented with recurrent epistaxis and right sided pulsatile tinnitus for 6 months. Nasoendoscopy revealed a large vascular mass in the nasal cavity. A MRI and angiogram were performed for further evaluation of the mass. Selected images of the MRI and angiogram were illustrated.
Diagnosis:
Juvenile Angiofibroma (JAF)
Discussion:
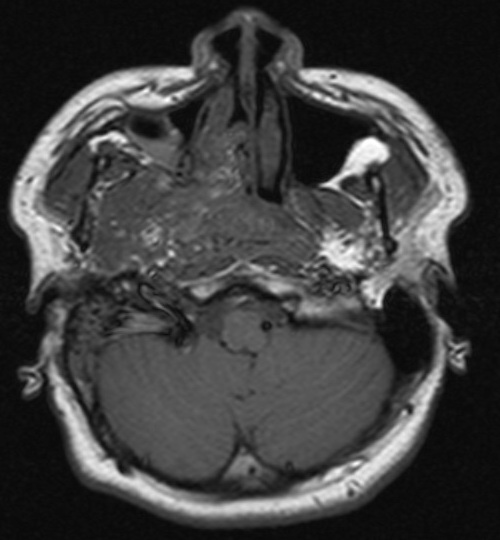
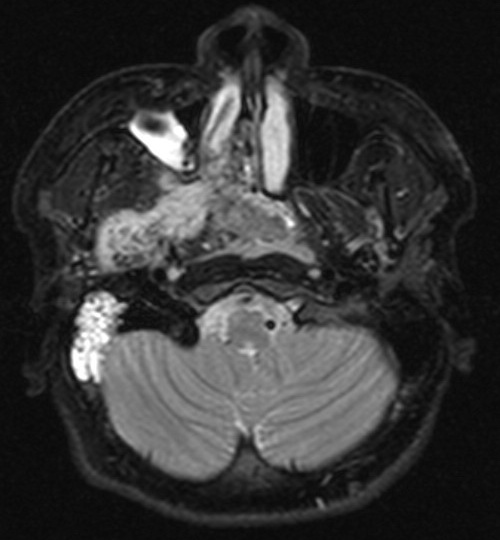
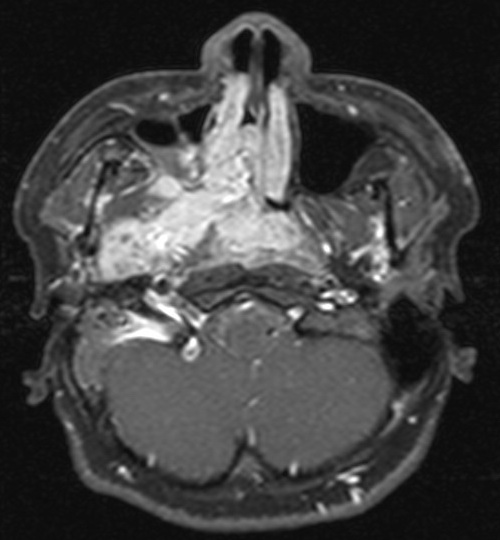
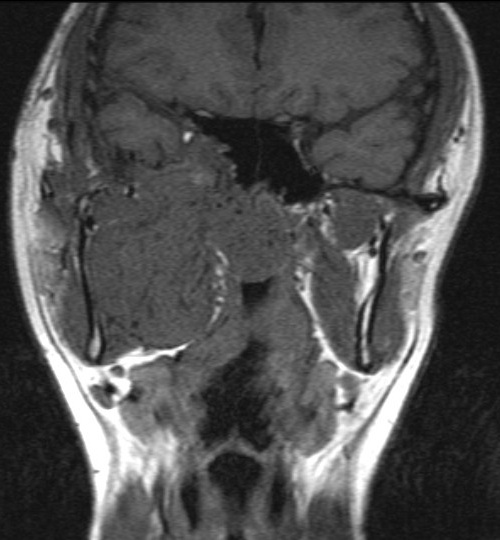
MRI shows a large lesion centered in right posterior nasal cavity with extension into right masticator space. The lesion is mainly intermediate signal in T1WI and hyperintense in T2WI. Multiple flow voids are seen within the lesion. Angiogram of right external carotid artery (ECA) shows a hypervascular lesion supplied by hypertrophied branches from right ECA.
Juvenile angiofibroma (JAF), also called juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma, is a benign vascular locally invasive nasal cavity mass found exclusively in adolescent males. If it is found in a female, genetic testing may reveal mosaicism. It originates in the sphenopalatine foramen. Large tumors are frequently bilobed or dumbbell-shaped, with one portion of the tumor filling the nasopharynx and the other portion extending to the pterygopalatine fossa. The lesion may extend to involve the masticator space, adjacent paranasal sinuses and middle cranial fossa.
Patient usually presented with recurrent epistaxis and unilateral nasal obstruction. Other symptoms include proptosis, nasal discharge and serous otitis media.
The MRI features of JAF include a T1 heterogenous intermediate signal lesion centered at posterior nasal cavity showing intense enhancement. The lesion often shows intermediate-to-high signal in T2WI. Small signal voids may be seen within the lesion. Angiographic findings include intense capillary blush with enlarged feeding vessels arising from ECA.
Treatment for JAF involves complete surgical resection using pre-operative embolization to reduce blood loss. Radiotherapy is used as an adjuvant to surgery for unresectable intracranial disease. Radiotherapy alone for cure is used in some centers. Hormonal therapy is controversial which shows tumor regression in some cases. However, feminization side-effects are undesirable in adolescent male.