Answer of February 2015
For completion of the online quiz, please visit the HKAM iCMECPD website: http://www.icmecpd.hk/
Clinical History:
6 month old boy with left frontal portwine stain since birth. Otherwise asymptomatic.
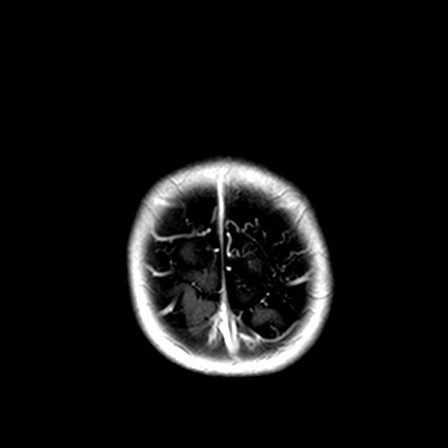
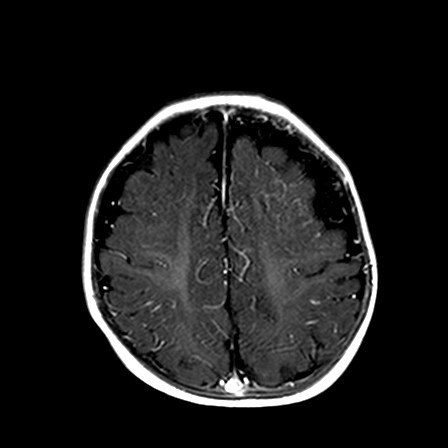
Fig 1. PD Axial
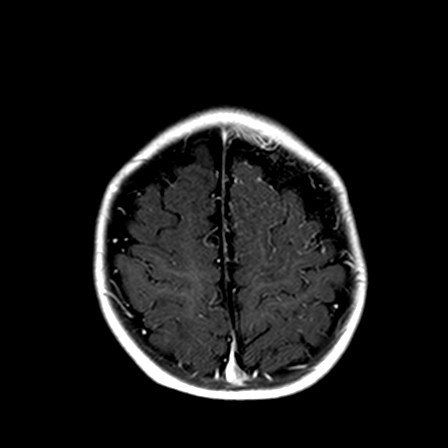
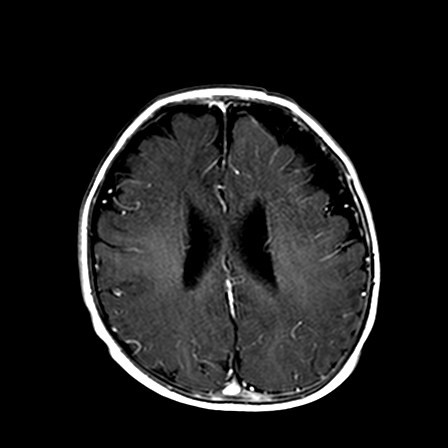
Fig 1. T1 with Gd contrast Axial
Diagnosis:
Sturge Weber Syndrome
Discussion:
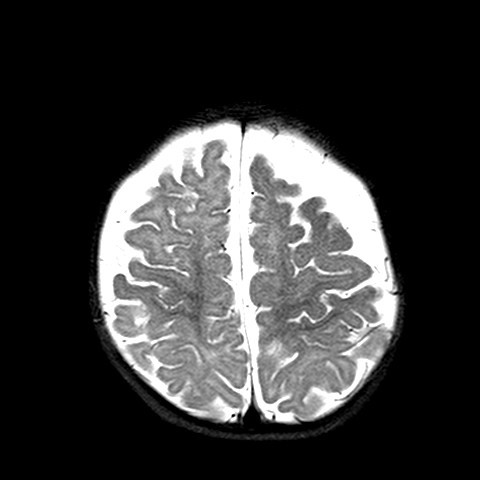
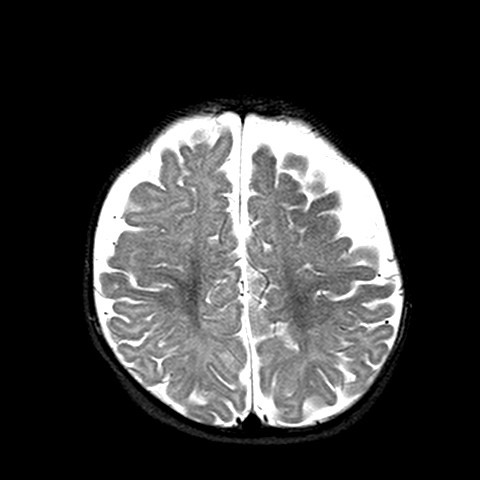
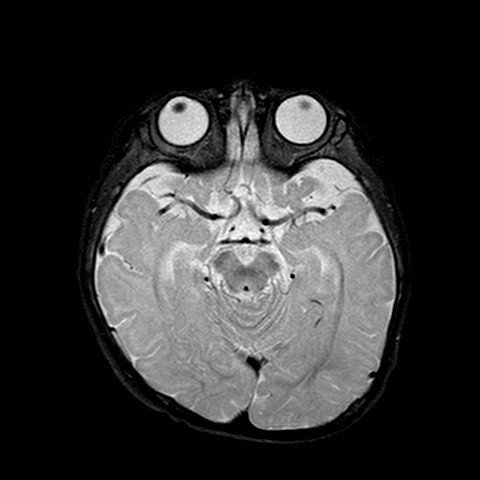
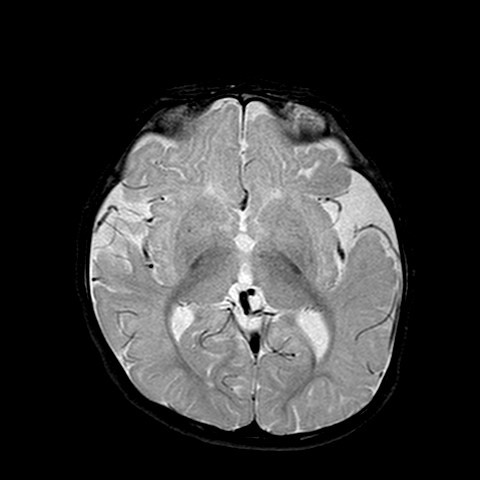
The MR brain shows advanced or accelerated myelination in left frontal lobe, associated leptomeningeal / pial enhancement. There is widening of the sulcal spaces in bilateral frontal, anterior temporal and anterior interhemispheric regions which appears slightly more marked on left frontal region. No definite internal displacement of cortical veins nor mass effect is noted. Features are suggestive of benign enlargement of the subarachnoid spaces with some degree of early volume loss of left frontal lobe. Globe and retina is normal.
Sturge weber syndrome is a non hereditary sporadic disease, which patient has angiomatosis involving face, choroid of eye, and leptomeninges. Patient may have mental deficiency or seizures.
Typical features on mature brain involves cerebral hemiatrophy with tramtrack gyriform calcification, ipsilateral choroid plexus hypertrophy, enlarged paranasal sinuses, thickening of skull vault, enlarged globe, retinal angiomatosis.
Changes are more subtle when the brain is immature, and often only detected on MR brain. Special feature in immature brain is accelerated myelination on the side with portwine stain, due to increased blood flow by pial angiomatosis. Pial enhancement would also be seen.