Answer of June 2024
For completion of the online quiz, please visit the eHKAM LMS website.
Clinical History:
A 68-year-old male of unremarkable past health, presented to the ENT surgeons for nasal blockage for years. Physical examination revealed left maxillary sinus polypoid lesion. A CT of the paranasal sinuses was done.
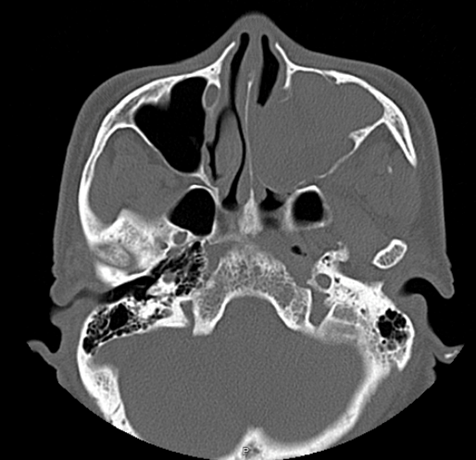
Axial bone window
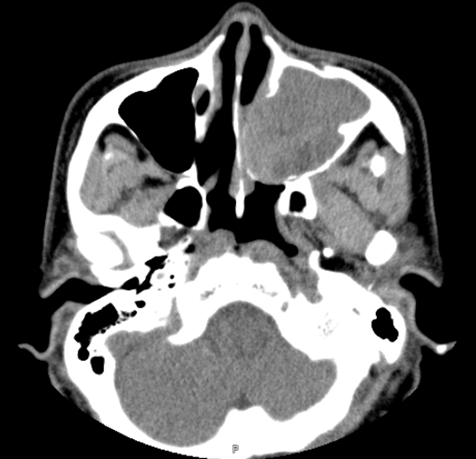
Axial soft tissue window
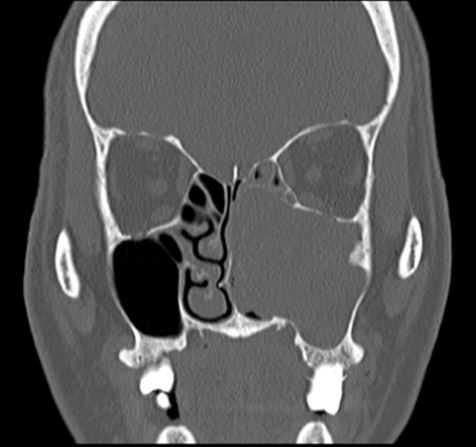
Coronal bone window
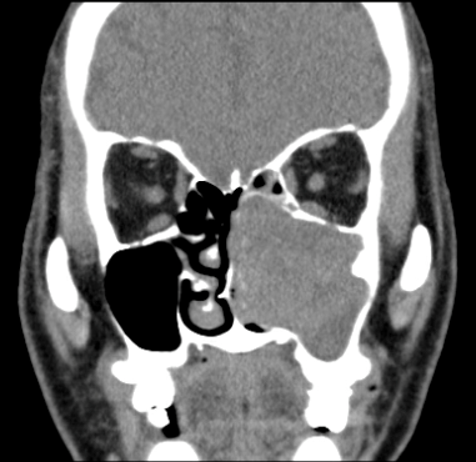
Coronal soft tissue window
DIAGNOSIS
Left maxillary sinus inverted papilloma
IMAGING FINDINGS
- Soft tissue mass within left maxillary sinus, with expansion of left maxillary ostia and extension into left nasal cavity.
- Bony stalk at lateral maxillary sinus wall.
- Bony remodeling of left maxillary sinus walls and turbinates.
DISCUSSION
Inverted papillomas are uncommon sinonasal tumours affecting mostly middle-aged men. Although benign, it is a locally aggressive neoplasm that also carries risk for malignant transformation, e.g. squamous cell carcinoma. In addition, it has high growth potential as well as recurrence rate. Therefore care has to be taken to ensure complete local resection.
Patients present similarly to sinusitis or other sinonasal masses, such as rhinorrhea, nasal obstruction or pain. They commonly originate from the lateral wall of nasal cavity, expanding the maxillary ostium and extending into the maxillary antrum.
On CT, this enhancing soft tissue mass could cause bony remodeling or even destruction as it enlarges, mimicking other lesions such as inflammatory polyps or even more aggressive tumours such as squamous cell carcinomas. More specific feature of intralesional calcifications are seen in less than half of the cases. It is important to look for a bony stalk, as seen in our case, as this focal hyperostosis denotes the point of origin of the lesion, which would be important to take note of and to remove during surgery to reduce recurrence.
On MRI, it demonstrates a distinctive convoluted cerebriform pattern of alternating lines of high and low signals.