Answer of December 2023
For completion of the online quiz, please visit the eHKAM LMS website.
Clinical History:
A
70-year-old lady complained of rapid worsening of left hip pain. The hip joint
culture was negative for bacterial growth. Joint aspiration was negative for
crystals. The serum level of autoimmune markers and fasting glucose were also
normal. A CT exam was performed and then repeated 7 months after.
The initial axial CT pelvis
The
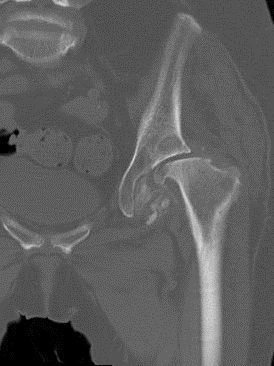
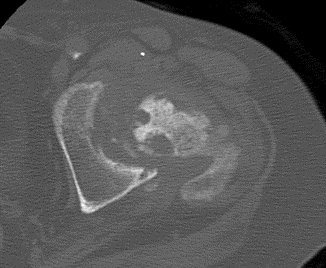
CT pelvis after 7 months (Coronal CT reformat and axial CT)
DIAGNOSIS:
Rapidly progressive osteoarthritis
IMAGING FINDINGS
The initial axial CT pelvis showed a normal left hip.
Coronal CT reformat and axial CT - The CT pelvis after 7 months showed gross destruction of the left hip with subchondral cyst formation in the left acetabulum, complete flattening of the femoral head and presence of multiple intra-articular loose bodies.
DISCUSSION:
RPOA is uncommon but is more frequently seen in practice because of the aging population. RPOA is a destructive arthropathy that occurs most commonly in elderly women but can also be seen in patients that have sustained trauma. The dramatic radiologic manifestations of RPOA can lead to diagnostic confusion with other arthropathies, infection, and osteonecrosis. RPOA is diagnosis of exclusion; need to exclude other potential causes (aspirate joint)
Natural History & Prognosis
Type 1 RPOA: weeks to months of joint pain, followed by JSN ≥ 2 mm in < 1 year
Type 2 RPOA: similar to Type 1 RPOA but with additional rapid progression of joint/bone destruction