Answer of December 2017
For completion of the online quiz, please visit the HKAM iCMECPD website: http://www.icmecpd.hk/
Clinical History:
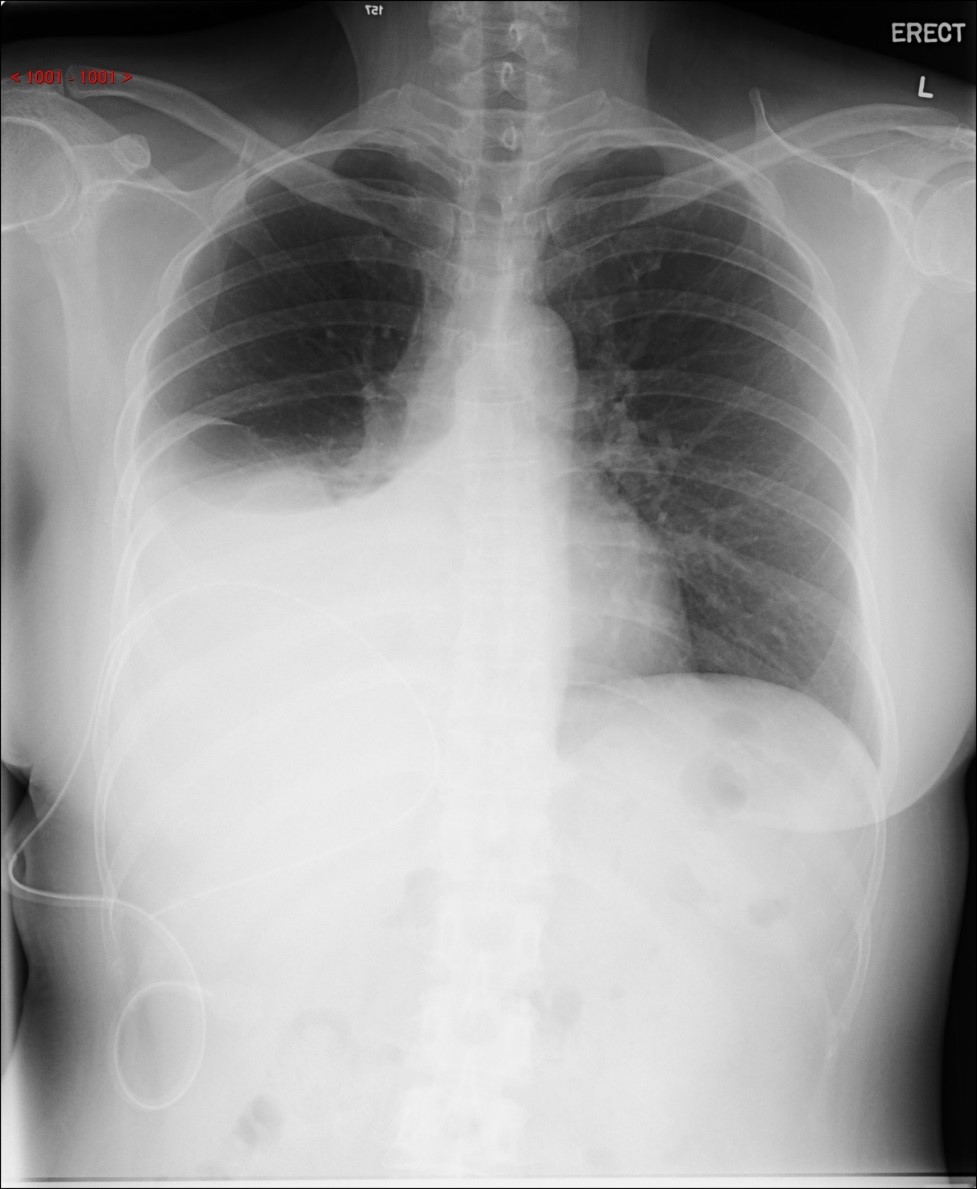
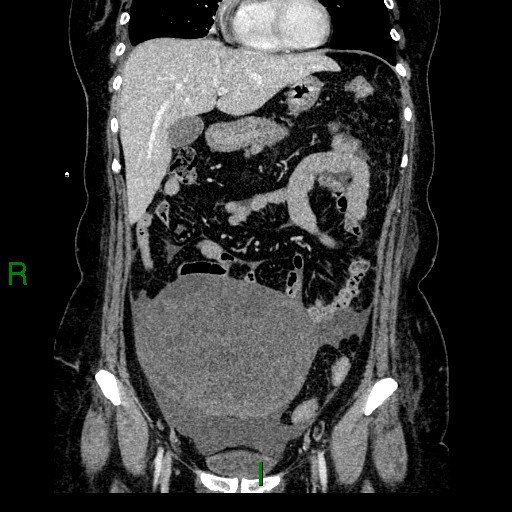
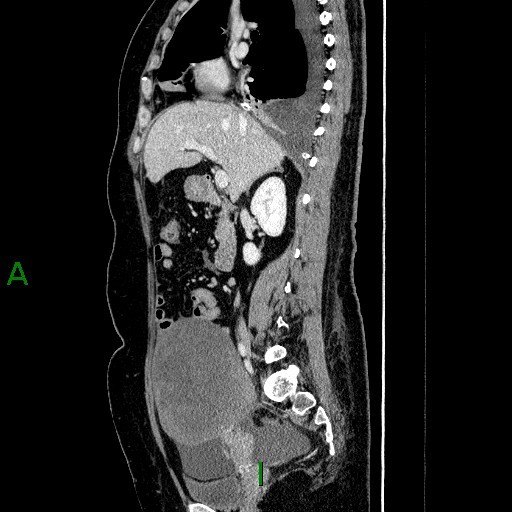
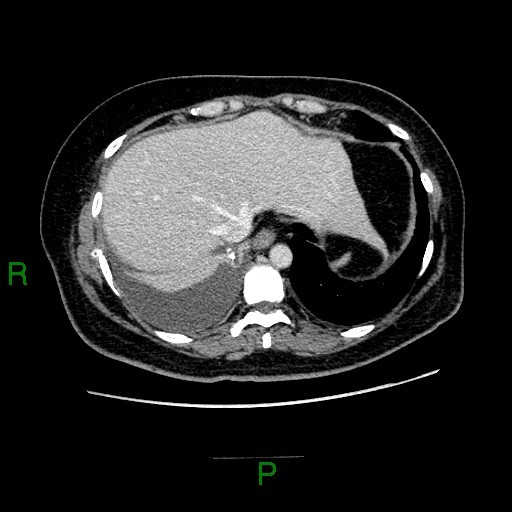
A 49 year old lady presented with moderate right pleural effusion. The CA-125 was 436 U/ml (normal level: <35 U/ml) U/ml). She was referred to us for CT thorax, abdomen and pelvis workup.
Imaging Findings:
CXR: Moderate right pleural effusion.
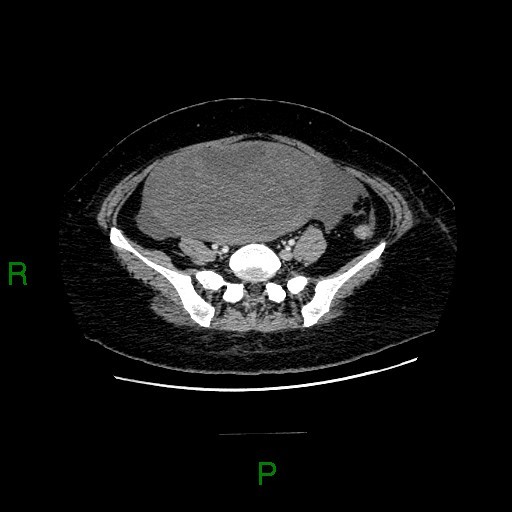
CT: a large heterogeneous enhancing solid mass at pelvis and lower abdomen. Small amount of ascites.
Diagnosis:
Meigs syndrome with ovarian fibroma
Discussion:
Meigs syndrome is defined as presence of ascites and pleural effusion in association with a benign ovarian tumour. The ascites and pleural effusion resolve after the tumour is removed.
In a review of 128 case of Meigs syndrome by Majzlin and Stevens, the most common (91.4%) tumours were fibromas or fibrothecomas. Less common tumours included benign granulosa cell tumours (4.7 %) and Brenner tumours (1.6 %).
One point to note for Meigs syndrome is that the presence of ascites and pleural effusion does not necessarily indicate the pelvic mass is malignant.
CA-125 is a tumour marker associated with ovarian carcinoma. However, elevation of CA-125 level has been reported in a variety of processes and it cannot be used to make a specific diagnosis.
Ovarian fibroma accounts for 4 % of all ovarian tumours, and it occurs most frequently in the 4th -6th decades of life. For imaging features, on ultrasound, fibromas most commonly manifest as solid, hypoechoic masses with ultrasound beam attenuation. On CT, ovarian fibromas usually manifest as diffuse, slightly hypoattenuating masses with poor, very slow contrast enhancement. On MRI, most fibromas are isointense to hypointense to uterine myometrium on T1- and T2 weight images. A band of T2 hypointensity separating the tumour from the uterus on all imaging planes is considered a characteristic feature. Fibromas usually show heterogeneous enhancement on post- contrast scan.
This patient underwent total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. Pathology confirmed right ovarian fibroma.