Answer of December 2015
For completion of the online quiz, please visit the HKAM iCMECPD website: http://www.icmecpd.hk/
Clinical History:
A 49-year-old lady is admitted for throat discomfort and dysphagia for 2 days. She is afebrile all along. Physical examination is unremarkable. The initial blood test is unremarkable with the WCC within normal limit.
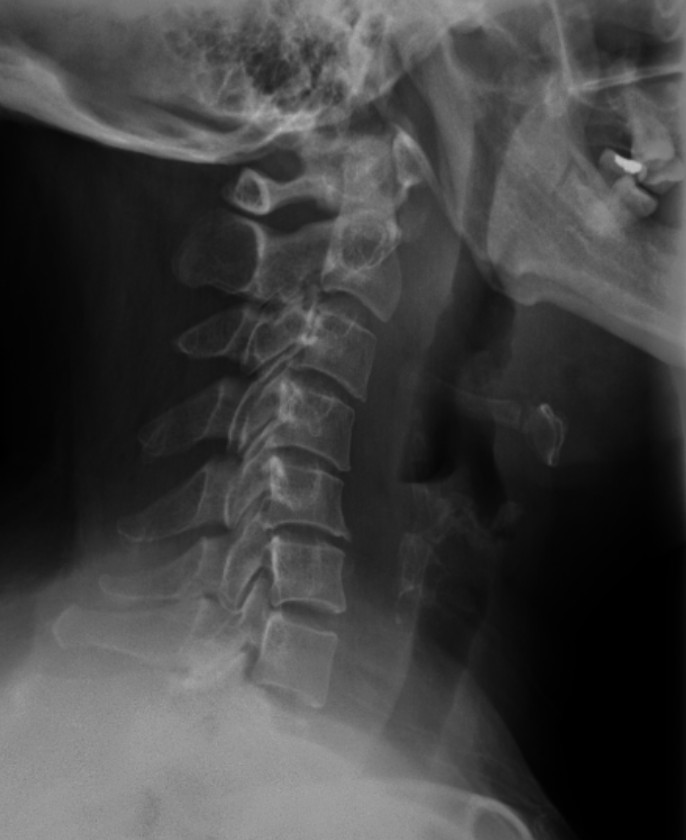
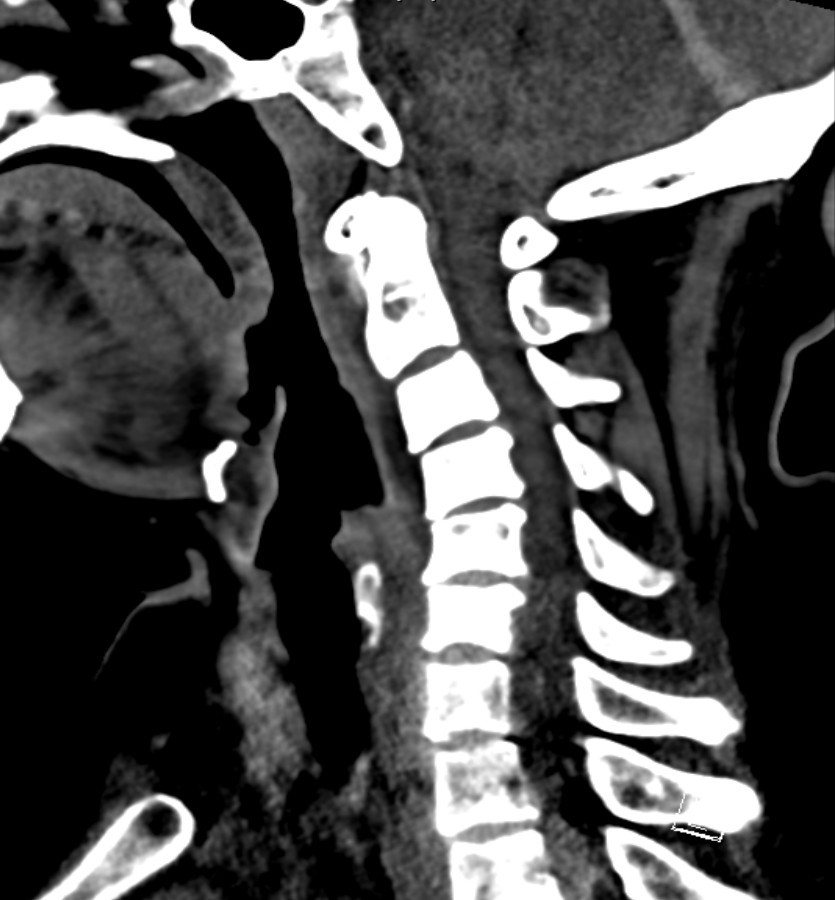
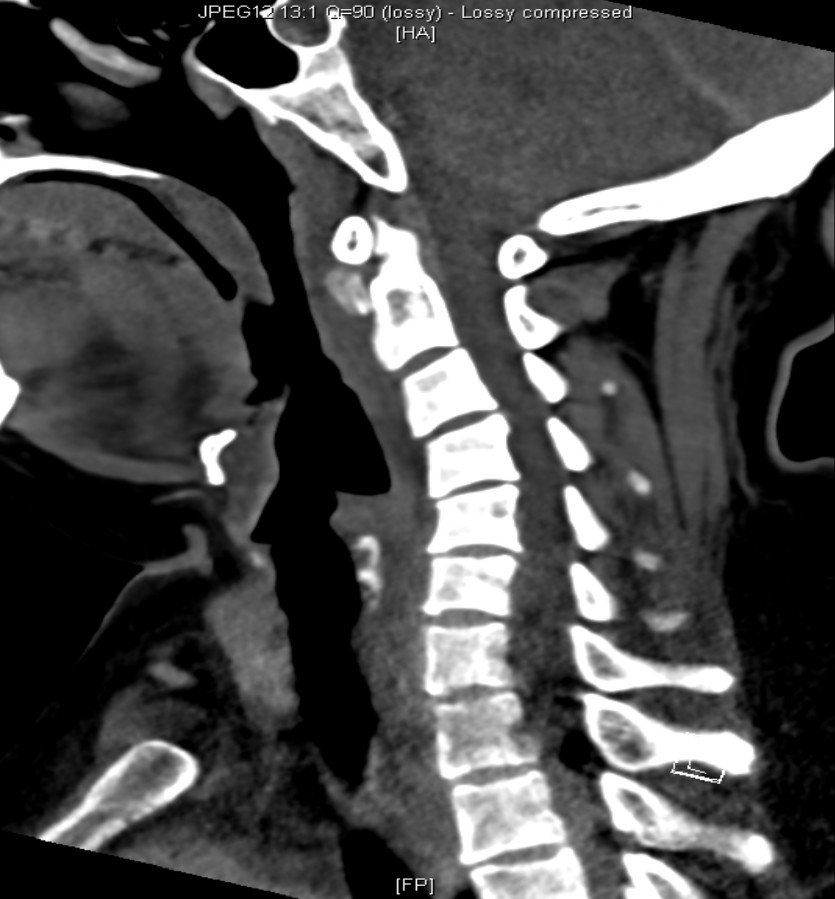
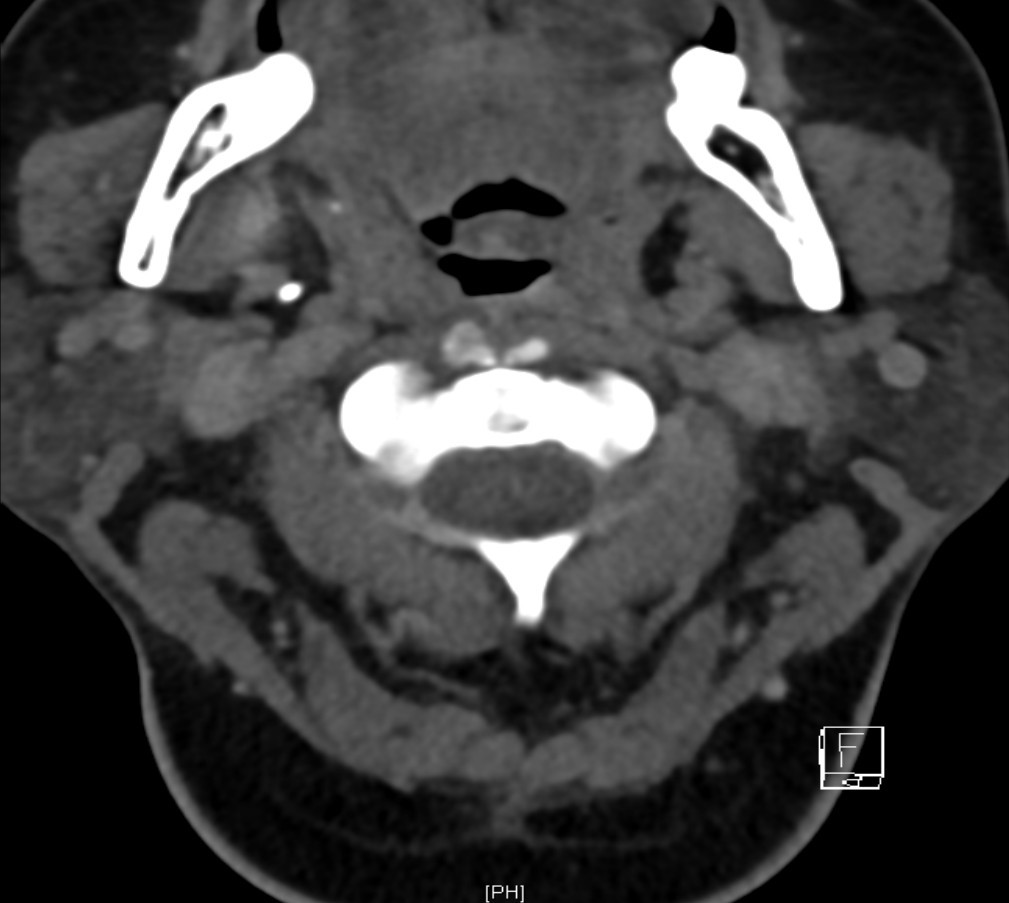
Xray cervical spine and lateral CT neck with contrast are obtained.
Diagnosis:
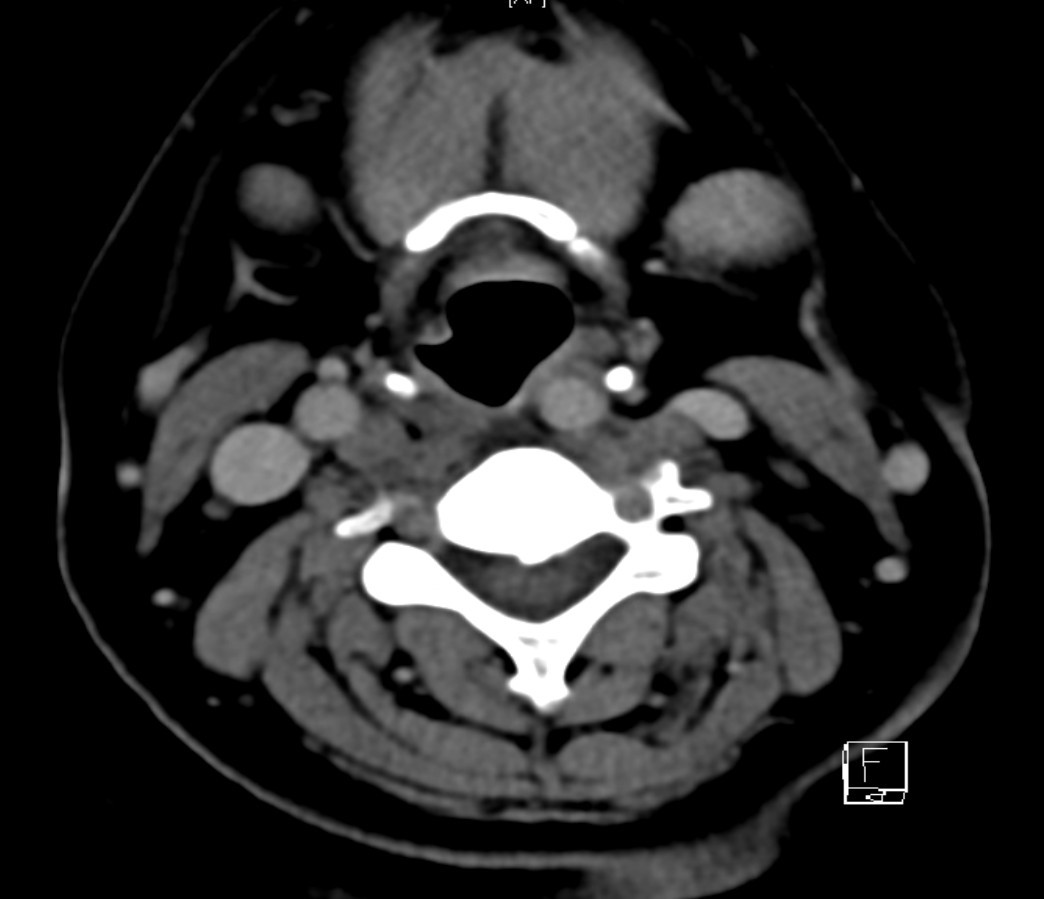
- CT : Thin rim of retropharyngeal fluid is seen anterior to C2-C5 vertebral bodies, with no definite surrounding rim enhancement detected. Abnormal Nodular & ovoid calcifications are seen embedded within the proximal fibres of longus colli tendon, anterior to C2 vertebral body.
- Diagnosis: Calcific tendinitis of longus colli muscle
Discussion :
Acute calcific tendinitis or longus colli tendinitis is an uncommon benign condition presenting as acute neck pain. Clinically, it can be misdiagnosed as retropharyngeal abscess, traumatic injury, or infectious spondylitis. The disease is caused by an inflammatory/granulomatous response to deposition of calcium hydroxyapatite crystals in the tendons of the longus colli muscle. The diagnosis is made radiographically by calcification anterior to C1-C2. Small retropharyngeal effusions and edema of the adjacent prevertebral soft tissues may also be seen. Enhancement around the effusion, adenopathy and bone destruction are usually absent and presence of these features should shift the diagnosis towards infection and abscess.