Answer of December 2008
Diagnosis:
Mucocele of appendix due to underlying mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
Discussion:
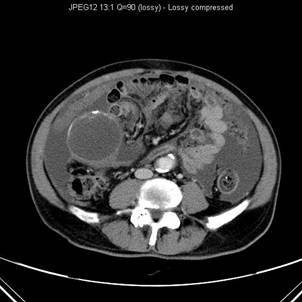
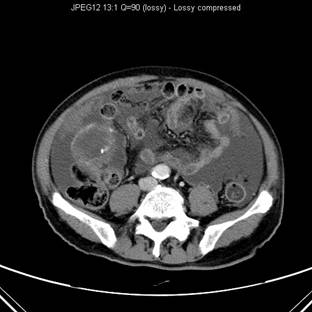
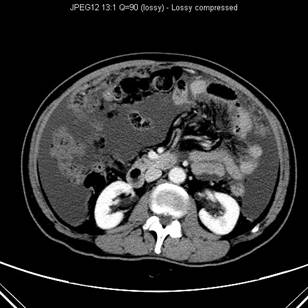
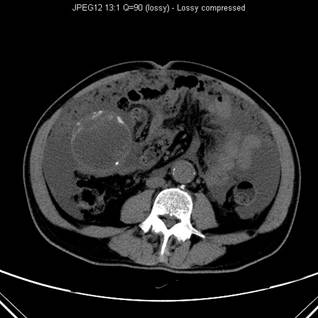
Contrast enhanced CT scan showed low attenuation mass with rim calcification at right lower quadrant of abdomen anterior to caecum. A normal appendix cannot be identified. Marked ascites with peritoneal nodules are also seen. Histological result revealed mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of appendix.
Mucocele of vermiform appendix is an uncommon abnormality found in 0.2%-0.3% of appendectomy specimen. It has been postulated that this abnormality is due to obstruction of the appendiceal lumen leading to accumulation of mucus. Mucocele of the appendix has a 4:1 Female predominance, and the mean age is 55 years (3). A palpable mass is present in up to 50% of cases. Associated symptoms include acute or chronic abdominal pain. Rarely, colicky pain may occur due to intussuception of the mucocele invaginating into the caecum. (2)
Mucocele of appendix is associated with colonic adenocarcinoma (6-fold increase) and mucin-secreting ovarian tumor (3).
At CT the typical finding in a cystadenoma of appendix is a round, thin wall, encapsulated cystic mass that communicates with the caecum. The attenuation of the content of the cyst may range from that of water to soft tissue, depending on the amount of mucin. Adjacent bowel loops may be displaced, but usually no periappendicular inflammation or abscess is seen. Soft tissue thickening and irregularity of the cystadenoma wall and surrounding fat are non-specific suggestive of malignancy, secondary inflammation or unusual pathological variation. Pseudomyxoma peritonei and extrappendiceal spread suggest malignancy.